If you're building apps with Next.js but feel like SEO is this mysterious black box, you're not alone. Most vibe coders who can now easily build different apps often struggle with the technical implementation of SEO. As a result, their apps never get mentioned in AI search engines like chatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini etc.
With AI-powered search engines like Google's AI Overviews, Perplexity, and even ChatGPT's search features taking center stage in 2025, optimizing for them isn't just about keywords anymore—it's about making your content crawlable, structured, and lightning-fast so AI can understand and cite it accurately.
Traditional SEO still matters, but AI search rewards sites with clear semantics, fresh data, and top-notch performance. In this guide, we'll discuss the technical SEO best practices using Next.js 15's App Router.
I'll keep things practical with code examples tailored to this site getranksmith.com (also built using Nextjs 15). No fluff—just actionable steps to boost your rankings without needing an SEO degree.
Whether you're launching a new app or tweaking an existing one, let's get your Next.js site AI-search ready.
Nextjs Rendering Techniques and Their Impact on Search Rankings
Rendering choices in Next.js directly affect how search engines (and AI crawlers) see your site. In the App Router, you can mix and match techniques for optimal SEO. Let's break it down.
Overview of Rendering Methods
Next.js 15 supports several approaches:
Static Site Generation (SSG): Pages are built at build time using export const dynamic = 'force-static';. Great for content that doesn't change often, like blog posts.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Renders on each request with export const dynamic = 'force-dynamic';. Ideal for personalized or real-time data.
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR): Combines SSG with revalidation (e.g., export const revalidate = 3600; for hourly updates). Keeps things fresh without full rebuilds.
Client-Side Rendering (CSR): JavaScript handles rendering in the browser. Use sparingly for interactive elements only. No really great for SEO crawlers.
Streaming and Partial Prerendering (PPR): Experimental in Next.js 15—prerenders a static shell at build time, then streams dynamic parts. Enable with experimental: { ppr: 'incremental' } in next.config.js.
Effects on Crawlability, Indexability, and Performance
Search engines love pre-rendered HTML because it's easy to crawl—no JavaScript execution needed.
SSG and ISR shine here: they deliver fully formed pages, improving index-ability and Core Web Vitals like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) under 2.5 seconds. SSR ensures up-to-date content for AI queries but can slow things down if overused, potentially hurting First Input Delay (FID).
CSR is a SEO no-go for core content pages. AI crawlers and bots might miss it entirely, leading to poor rankings.
For AI search in 2025, fast loads are crucial since AI models prioritize snippets from performant sites. PPR helps by blending static speed with dynamic flexibility, reducing time to interactive (TTI).
Recommendations for Next.js 15
Default to SSG/SSR for most pages to maximize SEO. For dynamic routes like user dashboards (if they are public and needs to appear in AI search), use SSR wrapped in Suspense for streaming.
//Example in app/blog/[slug]/page.js:
export const revalidate = 3600; // ISR: Revalidate every hour
export default async function BlogPost({ params }) {
const post = await fetchPost(params.slug); // Fetch data
return <div>{/* Render post */}</div>;
}This ensures AI crawlers get fresh, crawlable content without performance hits.
Implementing Metadata Correctly in Next.js 15 App Router
Metadata is your site's ID card for search engines—titles, descriptions, and more that show up in results and AI summaries. In Next.js 15 App Router, it's streamlined but powerful. It helps AI extract key info for rich snippets and answers. Poor metadata means your site gets overlooked in AI overviews.
In a fully rendered HTML page, you can see them as meta tags like these.
<meta name="next-size-adjust" content=""/><title>Ranksmith</title>
<meta name="description" content="The first comprehensive platform for tracking and optimizing your brand's presence across AI search engines."/>Implementation
In Next.js 15, you can either use static metadata or dynamically generate based on the content of different pages (do not use both on the same page).
In the app router, if you set metadata at the root layout.js, it will apply to all the pages that share that layout file. But each page can also export its own metadata and override the common layout metadata.
Static Metadata: This is the simplest way to implement metadata. Just export a metadata object from root app/layout.js to set metadata for the entire site (individual pages can override this by exporting their own static or dynamic metadata object)
// app/layout.js
import { Metadata } from 'next';
export const metadata: Metadata = {
metadataBase: new URL("https://getranksmith.com"),
title: "Ranksmith | Get discovered in AI Search",
description:
"The first comprehensive platform for tracking and optimizing your brand's presence across AI search engines.",
alternates: {
canonical: "https://getranksmith.com",
},
openGraph: {
title: "Ranksmith | Get discovered in AI Search",
description:
"The first comprehensive platform for tracking and optimizing your brand's presence across AI search engines.",
images: [{url: "https://getranksmith.com/og-image.png"}], //always use absolute url
},
};
};
export default function RootLayout({ children }) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body>{children}</body>
</html>
);
}Dynamic Metadata: Use generateMetadata async function for pages that have dynamic data. This is ideal for product pages and single blog post pages.
// app/blog/[slug]/page.js
import { Metadata } from 'next';
export async function generateMetadata({
params,
}: {
params: Promise<{ slug: string }>;
}): Promise<Metadata> {
const { slug } = await params; //params are a Promise in Next.js 15 and needs to be awaited.
const result = await getPost(slug);
const { title, description, image} = result.post;
return {
metadataBase: new URL("https://getranksmith.com"),
title,
description,
alternates: {
canonical: `https://getranksmith.com/blog/${slug}`,
},
openGraph: {
title,
description: description || "Ranksmith helps your business get discovered in AI Search like chatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini, and more.",
images: image, //can be an array of absolute image urls
},
};
}These are just the most commonly used metadata object parameters you should always have. But there are many other case specific metadata parameters that you use. Here is the link to official Nextjs metadata documentation page for all parameters and their usage.
Common Pitfalls
If you set a common metadata object on layout page and forget to override it with more specific metadata for dynamic pages like products or blog post pages, the static metadata will also apply to all the dynamic pages. Always set a common metadata object on layout and then override it with more specific metadata object on pages down in hierarchy.
Implementing JSON-LD Structured Data
What is JSON-LD?
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a form of structured data that tells AI and search engines exactly what your content means—not just what it says. Think of it as “marking up” articles, FAQs, products, or other content so machines can interpret it more accurately.
For example, JSON-LD can describe:
A person
An event
An organization
A movie
A book
A recipe
Many other entities
It’s implemented in a simple <script> tag using JSON format (e.g., "@type": "Article").
Why JSON-LD Matters
Improves AI Understanding
AI crawlers use JSON-LD to parse semantics, making content easier to understand than plain text.
Increases the likelihood of being cited in AI-generated results.
Boosts Search Visibility
Enables rich snippets in Google (e.g., ratings, FAQs, product details).
Enhances visibility in AI-powered search engines and generative results.
Strengthens E-E-A-T Signals
Helps establish Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, which are critical for both traditional SEO and AI-driven search.
Implementing JSON-LD in Next.js 15
Add a <script> in your layout or page component. You can set the parameters values statically or dynamically for dynamic pages. Example for an article in app/blog/[slug]/page.tsx:
// Inside the page component or a separate StructuredData component
import type { BlogPosting, WithContext } from "schema-dts";
const jsonLd: WithContext<BlogPosting> = {
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": post.title,
"description": post.excerpt,
"author": { "@type": "Person", "name": "Your Name" },
"datePublished": post.date,
"image": `https://getranksmith.com/images/${post.image}`,
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "RankSmith",
"logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "https://getranksmith.com/logo.png" }
}
};
return (
<>
<script
type="application/ld+json"
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: JSON.stringify(jsonLd) }}
/>
{/* Page content */}
</>
);Most incorrect implementations results from incorrect JSON object formatting. If you miss a comma or a double quote, it won't remain a valid object. That's why it is necessary to verify your json-ld implementation using Google Rich Test page
Setting Up robot.txt in Next.js
Robot.txt file tells different search engine crawlers and AI bots which pages they can or cannot crawl (read). Although it is a mere recommendation and the crawlers and bots maynot honor this, but it is still a good practice to have a robot.txt file in your root folder.
In Next.js, its really easy to set one up. Just create a file inside your /app directory with the following minimum content:
User-Agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: '/some-private-page-you-dont-want-to-index/'
Sitemap: https://getranksmith.com/sitemap.xmlYou can also dyniamically generate this using a function:
import type { MetadataRoute } from 'next'
export default function robots(): MetadataRoute.Robots {
return {
rules: {
userAgent: '*',
allow: '/',
disallow: '/some-private-page-you-dont-want-to-index/',
},
sitemap: 'https://getranksmith.com/sitemap.xml',
}
}More specific instructions about customizing your robot.txt file for different crawlers can be found in this official Nextjs documentation for robot.txt
Setting Up Sitemap in Next.js
The easier you make your site for AI crawlers and bots to discover and crawl, the better your chances of getting higher visibility. One file that helps immensely with this is your Sitemap file. Its an xml file that contains an array of urls to different pages on your site.
You can either do it statically or generate it dynamically like this in your /app directory
import type { MetadataRoute } from 'next'
export default function sitemap(): MetadataRoute.Sitemap {
return [
{
url: 'https://getranksmith.com',
lastModified: new Date(),
changeFrequency: 'yearly',
priority: 1,
},
{
url: 'https://getranksmith.com/about',
lastModified: new Date(),
changeFrequency: 'monthly',
priority: 0.8,
},
{
url: 'https://getranksmith.com/blog',
lastModified: new Date(),
changeFrequency: 'weekly',
priority: 0.5,
},
{
url: 'https://getranksmith.com/blog/optimize-nextjs-for-ai-search-appearance',
lastModified: new Date(),
changeFrequency: 'weekly',
priority: 0.5,
},
]
}Testing Your SEO Implementation
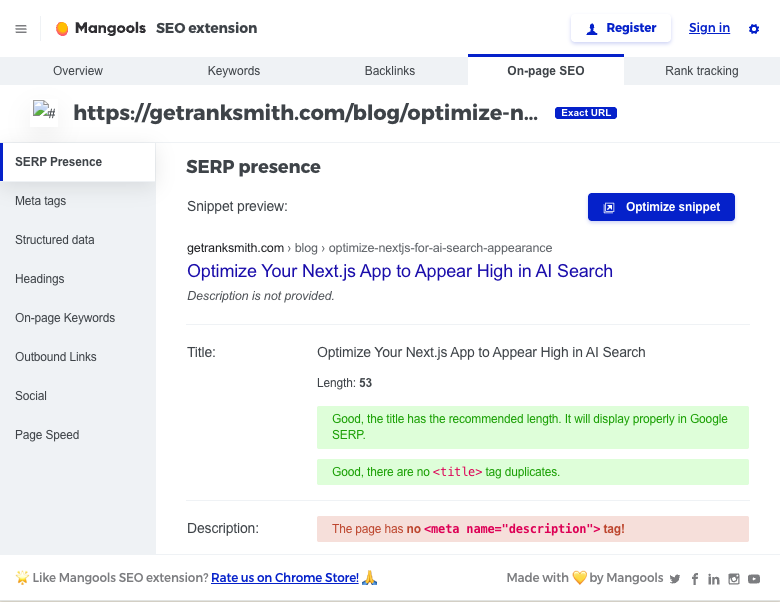
When you set everything up, it is important to verify if your technical implementations are all good to go. My favorite way to test all meta tags is using Mangools SEO extension.
Install the Mangools SEO extension for Chrome/Firefox—it's free and shows SERP positions, backlinks, on-page metrics, and page speed tips right in your browser.
Visit important pages on your site, click the extension, and verify title, description, OG tags, and structured data fields match your code. It flags issues like missing canonicals or in below example, a missing Description tag.
Other Tests
Schema: Google's Structured Data Testing Tool.
Mobile: Google's Mobile-Friendly Test.
AI-specific: Simulate with Screaming Frog, checking for JavaScript-rendered content. Debug hydration errors in dev tools which are common in dynamic metadata.
Conclusion
There you have it—your roadmap to making Nextjs app shine in AI search. Start with rendering and metadata, then layer on structured data and testing.
SEO is iterative, so monitor with tools like Ranksmith is essential. If rankings don't budge, team up with an SEO pro, but these technical wins will get you far. Drop a comment if you try this—happy coding! 🚀
